01Overview
02Technology Methods
03Project Workflow
04Case Studies
05Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
06Contact Us
Overview
CD Biosynsis is dedicated to offering high-quality enzyme immobilization services to customers worldwide. Enzyme immobilisation technology is an advanced biotechnology technique. This allows the enzyme to be anchored on a support in a way that increases the stability and reusability of the enzyme, while increasing its anti-inhibition capability. We specialize in enzyme isolation, purification and immobilization and industrialisation of biotransformation products. With different immobilisation strategies, including cross-linking, embedding and binding to supports, we are able to service multiple customers and optimize enzyme performance.
We aim to provide customers with consistent results and a top-notch service by constantly technologically developing and researching.
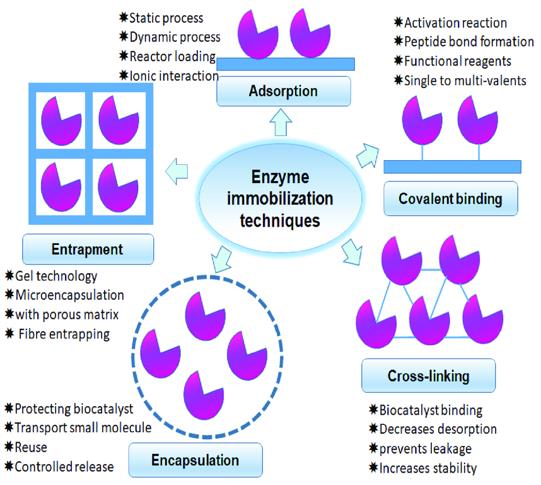 Types of enzyme immobilization techniques (Wan Yuen Tan, et al., 2023)
Types of enzyme immobilization techniques (Wan Yuen Tan, et al., 2023)
Technology Methods
Typical enzyme immobilisation techniques are the following:
Physical method:
- Adsorption process: The oldest enzyme immobilization process involves adhering the enzyme to the surface of a solid carrier. Most popular carriers are minerals (alumina, clay) and organic materials (starch, modified agarose, ion exchange resins).
- Embedding: Immobilization is carried out by embedding the enzyme into a gel or membrane. This procedure can further be divided into gels (silica sol-gel) or membrane reactors (membrane embedding).
Chemical method:
- Covalent binding: Activation is carried out through covalent reaction of the enzyme with active groups on the carrier. This is typically done using activated polymers (such as hydrogels containing diazo, carbodiimide or azide groups).
- Method of crosslinking: immobilization is done by bringing the cross-linker between the molecules of the enzyme or between the enzyme and the carrier to create three-dimensional network. This process helps the enzyme to be more stable and reusable.
Other methods:
- Electrostatic attraction: Immobilization occurs through the charge attraction between the enzyme and the carrier. Layered deposition (LbL) and electrochemical doping, for instance, operate on this principle.
- Multi-point covalent immobilization: By combining several covalent bonds at various vulnerable points in the enzyme molecule for a more stable and active enzyme.
Each of these approaches has its pros and cons, and the right immobilisation technology must be selected depending on the nature of the enzyme, the use case, and stability and re-usability requirements. By reasonable
by choosing and determining optimal immobilisation strategies, enzyme efficiency and commercial viability in industrial use can be significantly enhanced.
Project Workflow
Below is an overview of the service procedure of Enzyme Immobilization Service:
Start up of project and demand forecasting
Selecting the proper immobilization technique
Choice and optimization of carrier materials
Implementation of the immobilization procedure
Evaluation and optimization
Scale-up production and application development
- Start up of project and demand forecasting: In the first instance, you must communicate with the customers to get a detailed understanding of their requirements for enzyme immobilization solutions: enzyme needed, application profile (industrial, biosensors, medicine, etc.). and particular requirements for performance (i.e., stability, number of runs, etc). ).
- Selecting the proper immobilization technique: Choose the most appropriate immobilization technique based on customer requirement and enzyme nature. The most common forms of immobilisation are physical adsorption, covalent bonding, embedding, cross-linking etc. For instance, if the purpose is high stability and long durability, inorganic materials can better serve as carriers, and if the purpose is high activity and selectiveity, polymers can better serve.
- Choice and optimization of carrier materials: Choosing the appropriate carrier material is a major aspect of immobilization. Selection of carriers — These must be adapted to the effect they have on enzyme stability and catalytic activity (cost and availability). Since the past few years, advances in nanomaterials, smart polymers and new carrier materials have brought additional possibilities for enzyme immobilisation.
- Implementation of the immobilization procedure: Perform enzyme immobilization procedure based on immobilization procedure and carrier material selected. These could be the attachment of the enzyme to the carrier, cross-linkings, or the design of the immobilization parameters (temperature, pH, reaction time, etc. ).
- Evaluation and optimization: The immobilized enzyme must be assessed in terms of performance – activity recovery, stability, repeated applications, etc. According to evaluation results, changes to the immobilisation conditions or carrier material may be required to maximise the enzyme's activity.
- Scale-up production and application development: Once performance of the immobilized enzyme is confirmed at the lab level, it is possible to scale up the production and tailor application plans. This can be enzyme recovery, purification and end product development.
- Support and services: To provide ongoing technical support and services to customers to resolve challenges during the application of immobilized enzymes, and further developing products and services on the basis of customer's feedback.
Through the above process, we can offer customers full service from enzyme immobilization technology selection and application to performance evaluation and optimization so that customers can safely and reliably apply immobilized enzymes to any biocatalytic function.
Case Studies
Project background:
Starch is a key component, and this process needs to be biotransformed but the traditional enzyme-catalysed approach is expensive and inefficient. For efficiency and cost savings, a food manufacturer wants to use enzyme immobilization technologies to optimise starch conversion.
Solution:
We placed the amylase on a support frame of polyacrylamide. In this way, the enzyme does not have to be in the reaction and it can be reacted with which reduces enzyme consumption and price.
Result:
With the use of enzyme immobilization technology, the starch conversion efficiency increases by 30%, and the enzyme's service life increases by 5 times — saving production costs. Furthermore, since the enzyme is stable and reusable, all production steps are more manageable and cost-effective.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some commonly asked questions and answers for customers to understand Enzyme Immobilization Service we offer:
Q: What is enzyme immobilization?
A: Enzyme immobilization is the act of encapsulating an enzyme on a carrier, either physically or chemically, so that it can survive stable in a non-water-soluble solution and be reprocessed. This approach can increase enzyme stability and recycle rate, and reduce production costs.
Q: What are the predominant enzyme immobilization methods?
A: Typical techniques include: (i) binding of the enzyme to a commercial carrier, (ii) integration of the enzyme in an organic or inorganic polymer matrix, and (iii) cross-linking of the molecules of the enzyme. There are also adsorption, covalent bonding, encapsulation and cross-linking.
Q: What are the benefits of enzyme immobilization?
A: Enzyme immobilization enhances enzyme stability and recyclability, decreases cost, and enable enzymes to function at a greater pH and temperature range. Further, the immobilized enzyme can be used in other solvents and is more substrate specific and selective.
Q: What is the industrial use of enzyme immobilisation?
A: The enzyme immobilization process finds applications in medical, food, detergent, textile and pharmaceutical industries. They are used in biocatalytic reactions for biosensors, production of antibiotics, biodiesel and bioremediation.
Q: So how to select the enzyme immobilization protocol and carrier material?
A: The choice of enzyme immobilization technique and carrier material depends on the specific application required, enzyme type, process type, substrate type. For instance, if the application calls for high stability and longevity, inorganics are likely to be better. Other processes and materials may be required for applications where catalytic activity and selectivity are crucial.
Q: What are the benefits of enzyme immobilization services?
A: There are benefits of enzyme immobilization service:
- Enhance enzyme stability: Once immobilized, the enzyme is able to be active across a much greater pH and temperature range.
- Increased reuse rate: The immobilized enzyme can be reused reducing the production cost.
- Purified product: Embedded enzymes are easily separated and recovered ensuring purity of the product.
Q: So how to keep the enzyme stable when it's immobilized?
A: Making the enzyme stable once immobilized requires:
- Choice of the carrier: This factor plays a significant role in maintaining the enzyme stability and activity.
- Control immobilization states: temperature, pH level and reaction time, etc. Such conditions will affect the stability and function of the enzyme.
- Maintenance and testing: Test the enzyme's activity and stability periodically, and perform necessary maintenance.
Enzyme immobilization is a simple, effective, low-cost approach that preserves the enzyme's catalytic function and allows functions to be repeated. Enzyme immobilization technique research, optimisation and application development to ensure that your project goes as planned and produces the results that you desire.
Please feel free to contact us to discuss your specific needs and cooperation details.

































 Types of enzyme immobilization techniques (Wan Yuen Tan, et al., 2023)
Types of enzyme immobilization techniques (Wan Yuen Tan, et al., 2023)