Sustainable upgrading of plastics to biodegradable polymers in a synthetic microbial ecosystem
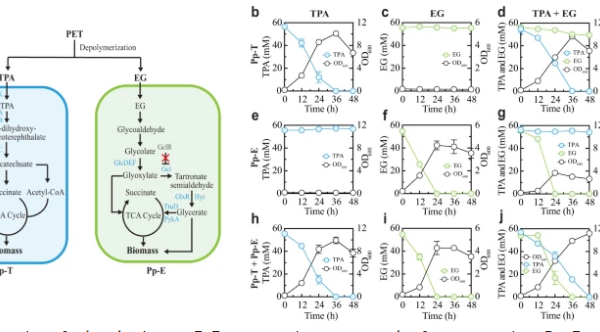
A synthetic P. putida consortium for simultaneous TPA and EG degradation. In response to the astonishing growth of global plastic pollution, researchers have developed a synthetic microbial ecosystem that can collectively upgrade plastics to the required chemicals. Researchers did not attempt to synthesize a single organism that could complete all the upgrading and recycling steps, but instead…